Imagine waking up to find your bank account drained, your identity stolen, and your private medical history circulating online—all because a company you trusted lost control of your data. Sadly, this isn’t dystopian fiction. It’s a routine news story.
From Equifax to Facebook, from hospitals to dating apps, data breaches are no longer exceptional—they are systemic failures of digital infrastructure. But the real threat is deeper: when data leaks occur, trust collapses, reputations erode, and ethical accountability often vanishes into legal grey zones. This article explores how breaches happen, why they persist, and what must change to make digital trust real again.
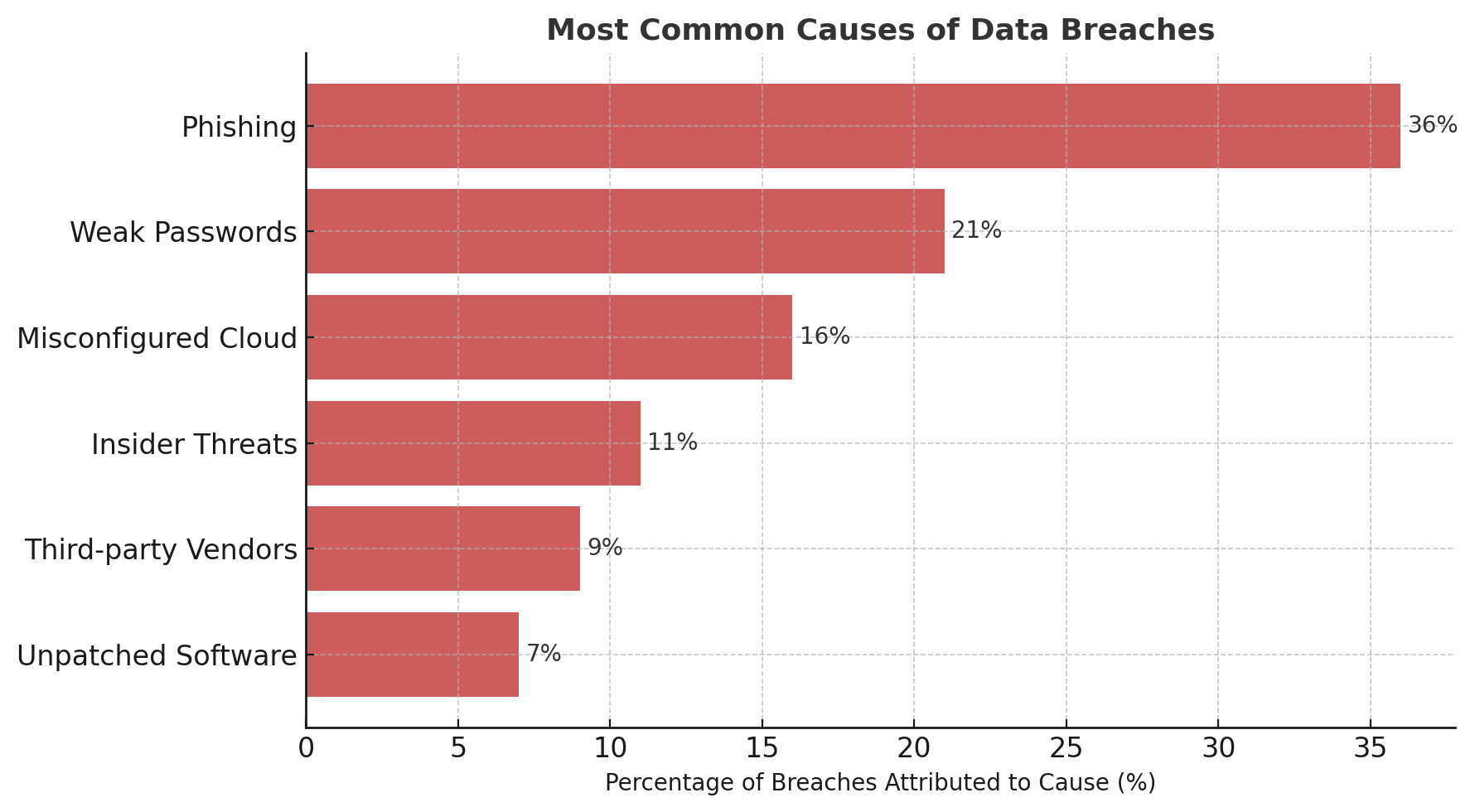
🧨 How Do Breaches Happen?
1. Phishing & Social Engineering
Hackers rarely "hack." They ask politely—by tricking someone into clicking a malicious link or entering credentials. These tactics bypass firewalls by targeting the weakest point: humans.
2. Weak Authentication
Reusing passwords, skipping MFA (multi-factor authentication), or relying on default credentials is a recipe for disaster—yet remains rampant across industries.
3. Misconfigured Cloud Storage
Exposed Amazon S3 buckets or unsecured databases are goldmines for attackers. These missteps often happen due to lack of cloud literacy among IT teams or overlooked defaults.
4. Third-party & Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The 2020 SolarWinds breach affected thousands—not because the company was attacked directly, but because one of its vendors was compromised.
5. Insider Threats
Sometimes, it’s not the hackers—it’s your own employees. Whether malicious or accidental, insiders can leak, steal, or mishandle sensitive data with devastating consequences.
⚖️ Ethical and Legal Dilemmas
-
Who owns the breach? When a company leaks user data, is it a technical failure, or a moral one?
-
Is consent meaningful? Most users "agree" to data use via unread Terms of Service. But should that waive liability?
-
When should the public be told? Many firms delay breach notifications to protect stock prices, at the expense of user safety.
Data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA attempt to create standards. Yet enforcement is inconsistent, and fines rarely match the damage caused.
🧩 Real-World Case: The Equifax Breach
In 2017, Equifax lost the personal data of 147 million people—including Social Security numbers and credit data. Why? A single unpatched Apache server vulnerability. The company failed to disclose the breach for weeks. Eventually, Equifax paid a $700M fine—but no executives faced criminal charges.
🧠 What’s the takeaway?
-
Poor patch management
-
Delayed disclosure
-
Lack of executive accountability
The system didn't fail. It worked exactly as it was built—to protect corporate assets, not consumer data.
🛡️ What Can Be Done?
For Organizations:
-
Zero-trust architecture: Assume no system or user is inherently safe
-
Regular audits and patch cycles
-
Third-party risk assessments
-
Incident response plans with legal + PR readiness
For Lawmakers:
-
Mandated breach disclosure timelines
-
Criminal penalties for willful negligence
-
Data ethics training for executives
-
Support for privacy-by-design development
For Individuals:
-
Use password managers + MFA
-
Don’t reuse passwords across services
-
Monitor credit and identity regularly
-
Think critically before sharing data online
🔮 Conclusion: Breaches Are Inevitable—Negligence Is Not
We cannot design a digital world without risk. But we can choose how we anticipate, respond, and compensate for failure. The true cost of a breach isn’t just financial—it’s moral, relational, and societal.
As more of our identities move online, the need for ethical data stewardship becomes not just a business imperative, but a civil one.







