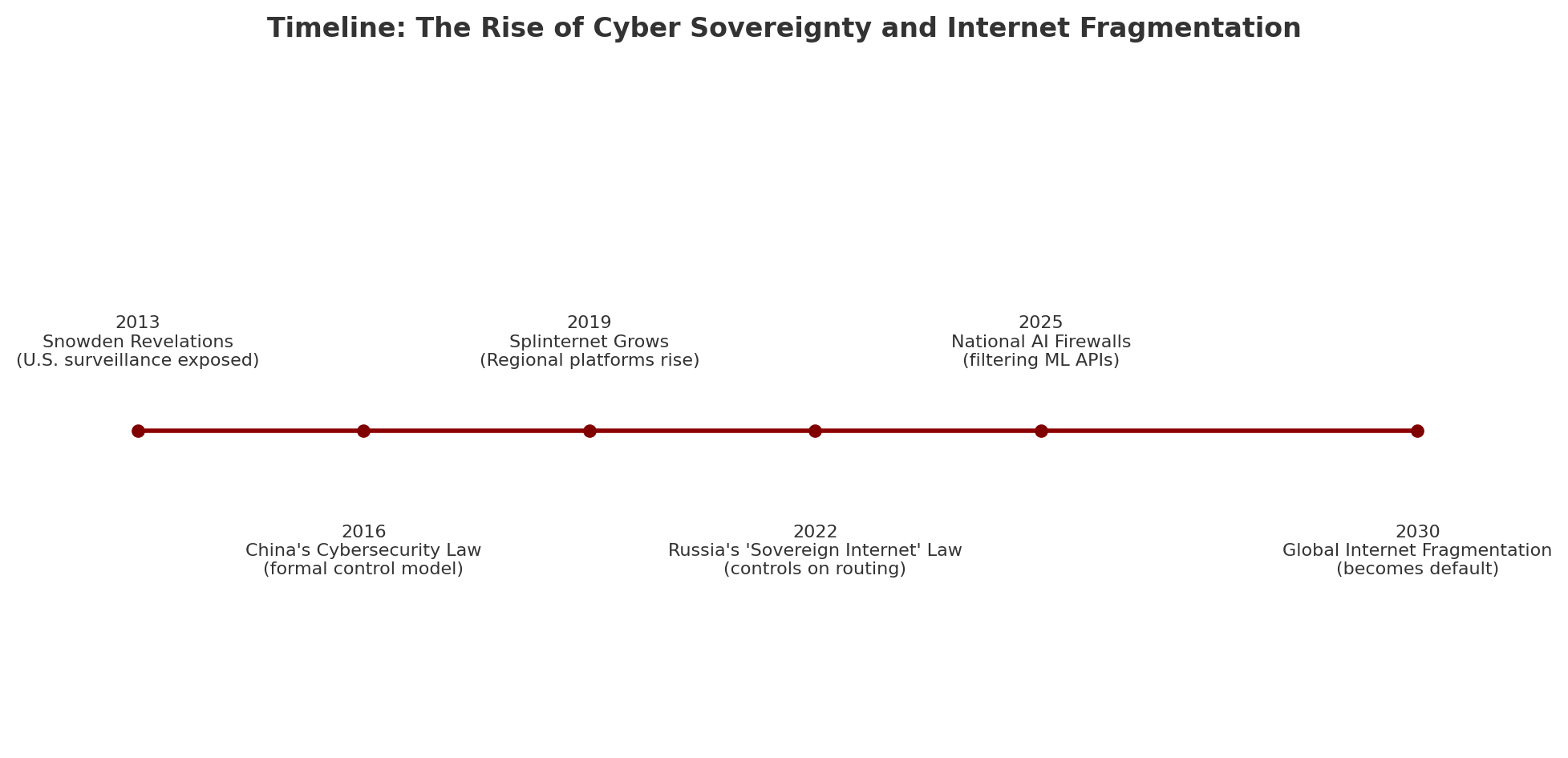
The internet was once envisioned as a global commons—a borderless space for knowledge, communication, and commerce. But that vision is fraying. In its place emerges a new paradigm: cyber sovereignty—the idea that each nation has the right to control its portion of cyberspace much like it governs its territory.
From Russia’s “sovereign internet” to China’s Great Firewall, and even Western debates over content moderation and data localization, a fragmented digital world is becoming not only possible—but inevitable. What does it mean when your experience of the internet depends on where you live, who governs you, and what servers you’re allowed to access?
This trend carries major implications for freedom of expression, digital rights, economic innovation, cybersecurity, and global cooperation. And it’s not just political—it’s deeply technological.
🕸️ What Is Cyber Sovereignty?
Cyber sovereignty is the assertion of state control over data flows, infrastructure, and online behavior within a nation’s borders. This includes:
-
Censorship and filtering
-
Mandated data localization
-
Control of DNS and routing
-
Platform bans and national alternatives
While defenders argue it's about digital self-determination, critics see it as digital authoritarianism cloaked in sovereignty.
🔍 Fragmentation in Practice
🇨🇳 China’s Model
-
Great Firewall blocks Western platforms (Google, Facebook, etc.)
-
Promotes domestic giants like Baidu, WeChat, Alibaba
-
AI content filters + strict real-name registration
🇷🇺 Russia’s Sovereign Internet
-
Created infrastructure to disconnect from the global web
-
DNS routing under government control
-
Blocks foreign media and platforms in real-time
🇪🇺 The Brussels Effect
-
GDPR enforces data protection extraterritorially
-
Push for digital sovereignty with local cloud providers and AI standards
🇺🇸 Techlash & Bans
-
Rising calls to ban TikTok, Huawei
-
Disputes over Section 230, content moderation, and encryption
⚖️ What’s at Stake?
🌐 Open Internet vs Digital Nationalism
The original internet vision—decentralized, open, permissionless—is now colliding with national interest.
🔓 Security or Control?
Cyber sovereignty is often justified in the name of security. But where’s the line between defense and surveillance?
💰 Innovation Divide
Fragmentation may lead to technical incompatibility across regions. Can global platforms survive in splintered standards?
🔮 Looking Forward
By 2030, the internet may look less like a network and more like a patchwork of connected intranets, with cross-border gateways tightly regulated.
Think of it as the "splinternet"—a world where tech stacks, regulations, and access diverge by nation-state logic.
Expect:
-
National app stores
-
Country-level AI firewalls
-
Blockchain-based digital IDs tightly tied to citizenship
-
Regional content laws enforced by machine learning
🧾 Conclusion: Can the Internet Stay Global?
Cyber sovereignty is no longer theoretical—it’s reshaping infrastructure, policy, and the user experience. Whether we’re headed toward a safer, more autonomous web, or a fractured world of digital silos, depends on how the global community responds.
The future of the internet will be decided not just by engineers—but by lawmakers, courts, activists, and all of us who log in daily.
🆕 Latest Updates on Cyber Sovereignty (September 2025)
-
China expands its digital firewall. Reports indicate Beijing is tightening controls on foreign AI platforms, requiring all AI models operating in China to undergo state “alignment audits.” This effectively creates an AI-specific Great Firewall.
-
Russia tests “Runet isolation drills.” Russian regulators carried out another nationwide stress test to simulate disconnecting from the global internet, citing “national resilience.” Activists warn this is a step toward permanent decoupling.
-
EU pushes forward with Digital Sovereignty Act. In Brussels, lawmakers advanced a proposal that would mandate European data to be stored and processed on EU soil, intensifying debates over data localization.
-
U.S. revisits TikTok ban. The White House is once again considering a nationwide ban or forced divestiture of TikTok citing national security risks, underscoring the geopolitical dimension of platform control.
Personally, I see cyber sovereignty as both understandable and deeply troubling. On one hand, nations have legitimate reasons to secure their infrastructure and protect citizens’ data. But what we’re witnessing now goes far beyond defense—it’s the construction of digital borders that erode the very essence of a global internet.
I believe that if this trend accelerates, we won’t just face a “splinternet” of different regulations—we’ll face entirely incompatible digital ecosystems. This won’t make us safer; it will make collaboration harder, innovation slower, and censorship easier.
The EU’s focus on privacy-driven sovereignty is, in my view, the least harmful path, since it still operates within a rule-of-law framework. But authoritarian models from China and Russia normalize the idea that control equals security—a dangerous precedent.
In short, I think the internet’s future hinges on whether democratic societies can strike a balance: safeguarding data and security without dismantling openness. Right now, the balance is tipping toward fragmentation, and I find that concerning.
👉 Cyber sovereignty is no longer theory—it’s policy. And unless there’s a strong push for interoperable global standards, I fear the next decade will lock us into digital borders that are far harder to tear down than physical ones.