Our world is bound together by a web of signals. Every video call, online transaction, and AI prompt relies on a complex communications infrastructure that’s evolving faster than ever. From 2G voice calls to 5G smart cities, connectivity isn’t just improving speed—it’s reshaping how we live, work, and sense the world.
With 5G rolling out globally, attention is already turning to 6G—a network that promises not just bandwidth, but awareness. And what comes after may blur the boundaries between communication, intelligence, and environment.
Understanding what’s next in connectivity is essential—not just for tech enthusiasts, but for anyone navigating a future where latency, spectrum, and sensing are as vital as electricity.
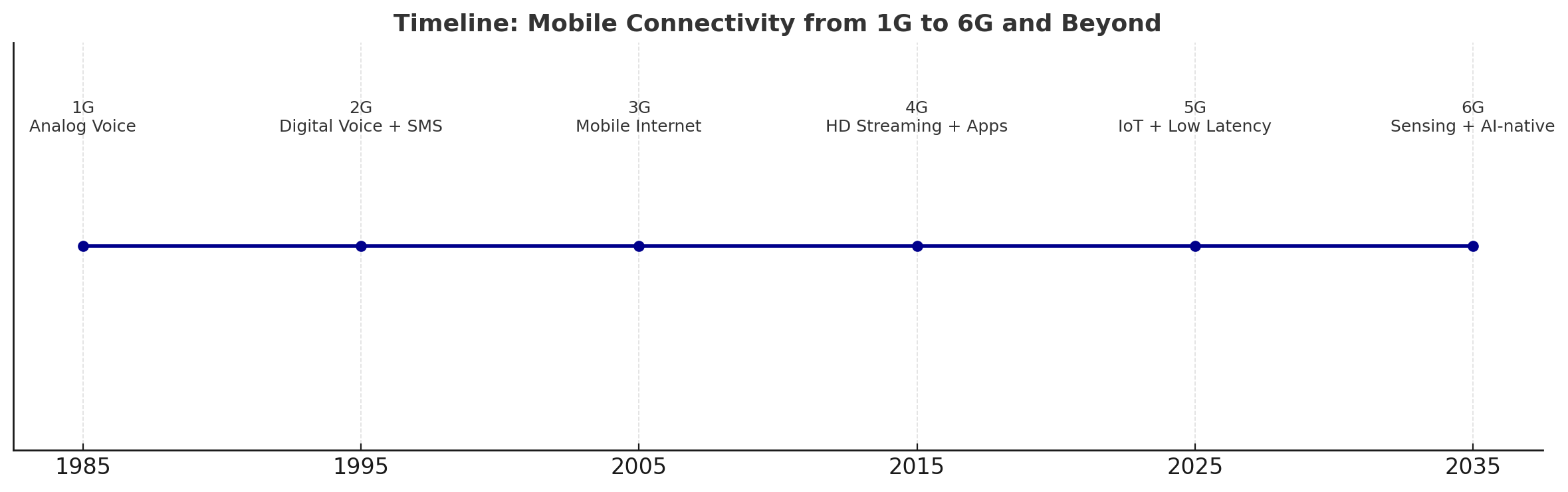
📶 The Evolution of Mobile Networks
Let’s take a quick look at how far we've come:
-
1G (1980s) – Analog voice
-
2G (1990s) – Digital voice and SMS
-
3G (2000s) – Mobile internet access
-
4G (2010s) – HD video, streaming, apps
-
5G (2020s) – Real-time IoT, low latency, edge computing
Each generation has reduced latency, expanded capacity, and unlocked new economies. But the leap to 6G is less about "more speed"—and more about changing what networks actually do.
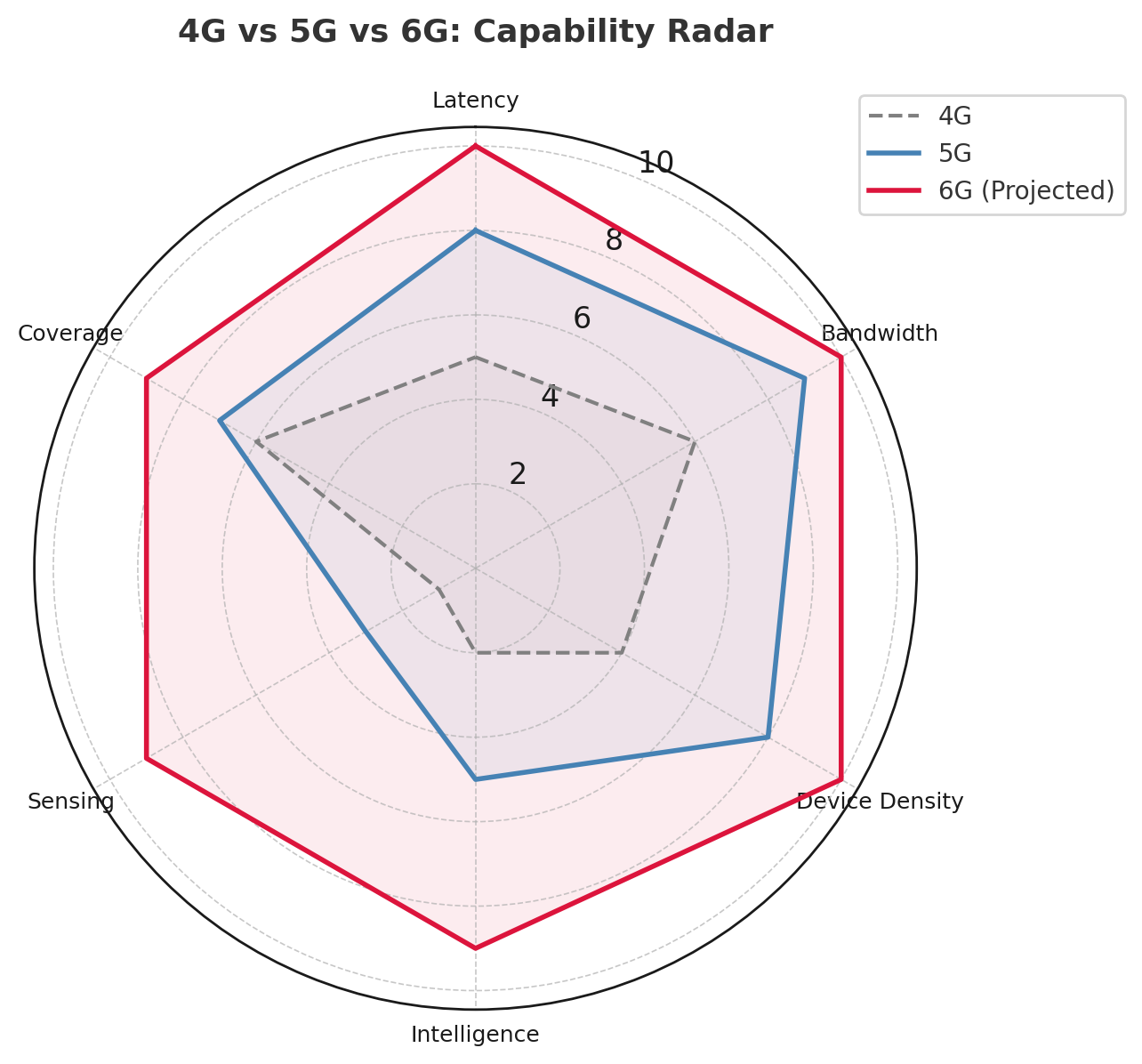
🚀 What Will 6G Actually Do?
Expected around 2030–2035, 6G goes far beyond streaming or downloads. It’s envisioned as a “Cognitive Network”—a fabric that senses, learns, and adapts in real-time.
Core Features:
-
📡 Terahertz Frequencies for ultra-high-speed data (>1 Tbps)
-
🧠 AI-native Networking where machine learning optimizes traffic flow autonomously
-
🌐 Network Sensing that turns infrastructure into real-time environmental sensors
-
⚡ Ultra-low Latency (<1ms), enabling true tactile internet (remote surgery, haptics)
-
🛰️ Non-terrestrial Integration (satellites, drones, high-altitude platforms)
Use cases include:
-
Autonomous mobility that reacts in milliseconds
-
Holographic meetings with 3D presence
-
Remote factories powered by real-time digital twins
-
Climate sensing through radio waves
📉 Challenges Along the Road
The promise of 6G is huge—but so are the barriers:
-
Power consumption: Terahertz bands require more energy and cooling
-
Hardware redesign: New chips, antennas, and spectrum access models
-
Security risks: Ubiquitous sensing could mean ubiquitous surveillance
-
Inequality: As tech evolves, access may deepen the digital divide
6G also demands a rethinking of infrastructure—from tower placement to cloud edge architecture.
🧾 Conclusion: A Hyperconnected Future?
As 5G matures and 6G looms, we’re moving toward a world where connectivity is ambient—woven into buildings, vehicles, even clothing. It's a future where your network doesn’t just send data—it understands context, predicts intent, and reacts in real time.
But as networks become smarter and more powerful, we must ask: Who controls them? Will connectivity serve public good—or commercial surveillance? Can infrastructure be resilient, equitable, and ethical all at once?
The answers will shape not just our technology—but the texture of our daily lives.
📰 What’s New in Connectivity & 6G
-
Chinese researchers unveiled a new “all-frequency” 6G chip that can handle multiple spectrum bands and deliver speeds over 100 Gbps. It’s a proof of concept toward seamless, high-speed, multi-band devices.
-
Ericsson has laid out a timeline: technical studies for 6G standardization begin in August 2025, with normative work starting around 2027.
-
NIST (USA) published a vision for 6G that centers on AI, security, and Open RAN as pillars of future networks.
-
On the infrastructure side, Northeastern researchers announced advances in tiny technologies (using metamaterials) to help alleviate congestion and spectrum pressure — which will matter both for 5G-advanced and early 6G systems.
-
India’s IIIT-N (Naya Raipur) secured a government grant to prototype cell-free communication in a 6G context — that is, moving away from cell towers toward a distributed access point model to deliver uniform coverage.
-
Meanwhile, in 5G land, operators are pushing 5G Standalone (SA) upgrades (cutting dependency on 4G), expanding private 5G for enterprises, and fusing AI into network optimization to boost performance and efficiency.
🧠 My Take: What I Think the Road to 6G (and Beyond) Will Look Like
Having watched these trends for a while, here’s how I see the next decade of connectivity unfolding — and what I worry could go wrong.
What I Expect to Happen
-
6G won’t just be “faster 5G”: It will increasingly be about network awareness, sensing, and integration. It will not only carry data but understand context (environment, movement, devices) in real time.
-
Hybrid networks (terrestrial + non-terrestrial) will be the norm. Satellites, high-altitude platforms, drones, and ground infrastructure will interlock to provide coverage everywhere.
-
Devices will get smarter and more adaptive. Chips will manage multiple frequency bands dynamically. Upload/download, sensing, and communication will converge.
-
Edge intelligence will be critical. To reduce latency, a lot of AI, prediction, and adaptation must happen close to the user — not in distant clouds.
-
Standardization is a long tail game. We’ll see multiple competing frameworks initially. The 2025 start date for technical work is just the beginning.
-
Access equity will be a central battleground. Unless deployment cost is managed, advanced connectivity may deepen divides — between regions, classes, urban/rural zones.
-
Privacy, governance, and surveillance risk will escalate. As networks sense more (user movement, environment, biometrics), protecting autonomy and data rights will become a major political issue.
What I’m Worried Will Go Wrong
-
Overpromising and hype: If 6G is marketed as “instant everywhere intelligence” before infrastructure and deployment catch up, we’ll see backlash and distrust.
-
Energy and efficiency constraints: High-frequency bands, dense antenna arrays, continuous sensing — all that may demand power and cooling that are infeasible in many places.
-
Fragmentation and silos: If every country, company, or consortium defines its own 6G standards or “walled gardens,” interoperability and global scale suffer.
-
Surveillance states: The sensing capabilities of 6G could become tools for monitoring and control unless built with strong privacy and civil safeguards.
-
Uneven rollout: Big metros, wealthy regions, and strategic corridors will pull ahead; remote or low-income regions might lag decades behind.
✅ Conclusion
We’re not just moving to a “better 5G.” We’re inching into a future where networks themselves become aware, predictive, and ambient. The technical building blocks are emerging now — smart chips, AI-native RAN, distributed access models — but the full vision of 6G is still being sketched.
In my view, the next decade is not about chasing raw speed. It’s about building connectivity that thinks, feels context, and adapts. But success depends not just on innovation — but fairness, governance, and vision. If we get that balance right, we may walk into a future where networks become as foundational as water or electricity — if we don’t, we risk building a hyperconnected world that’s unequal, opaque, and intrusive.