From Steam to Smart: A Snapshot of Industrial Evolution
Let’s trace the waves of industrial revolutions to understand where automation fits:
1st Revolution (18th century) — Mechanization (steam power, textile machines)
2nd Revolution (19th century) — Mass production (electricity, assembly lines)
3rd Revolution (20th century) — Digital automation (computers, robotics)
4th Revolution (21st century) — Smart automation (AI, IoT, machine learning)
We are now firmly in the fourth industrial revolution, where machines don't just execute—they learn and optimize.
How Automation Is Reshaping Factories
🦾 1. Intelligent Robotics
Modern robots are no longer limited to repetitive welding or painting. Cobots (collaborative robots) now work safely alongside humans, adapting in real-time using sensors and vision systems.
-
Example: BMW uses AI-equipped robots to handle delicate parts assembly, reducing error rates and improving speed.
-
Impact: Increased safety, consistency, and 24/7 productivity.
📊 2. Predictive Maintenance with AI
Instead of reactive repairs, factories now use machine learning to predict failures before they happen.
-
Example: Siemens uses AI to monitor vibration and temperature data to forecast turbine issues weeks in advance.
-
Impact: Downtime reduced by 30–50%, saving millions annually.
🌐 3. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
Connected devices enable machines to "talk" to each other, creating a smart, self-regulating production environment.
-
Example: GE’s Brilliant Factory connects every stage—from supply chain to quality control—via IoT sensors and dashboards.
-
Impact: Real-time visibility, agile adjustments to demand, reduced waste.
🧠 4. AI-Driven Quality Control
Vision systems powered by AI can detect micro-defects invisible to the human eye, learning from previous errors.
-
Example: Foxconn uses AI cameras to scan electronic components for millimeter-scale flaws at lightning speed.
-
Impact: Higher quality, fewer recalls, greater customer trust.
🔁 5. Dynamic Supply Chain Management
Automation is extending beyond the factory floor to inventory and logistics.
-
Example: Amazon’s warehouses use AI-powered robots and algorithms to manage stocking, packing, and shipping.
-
Impact: Faster order fulfillment, optimized inventory levels.
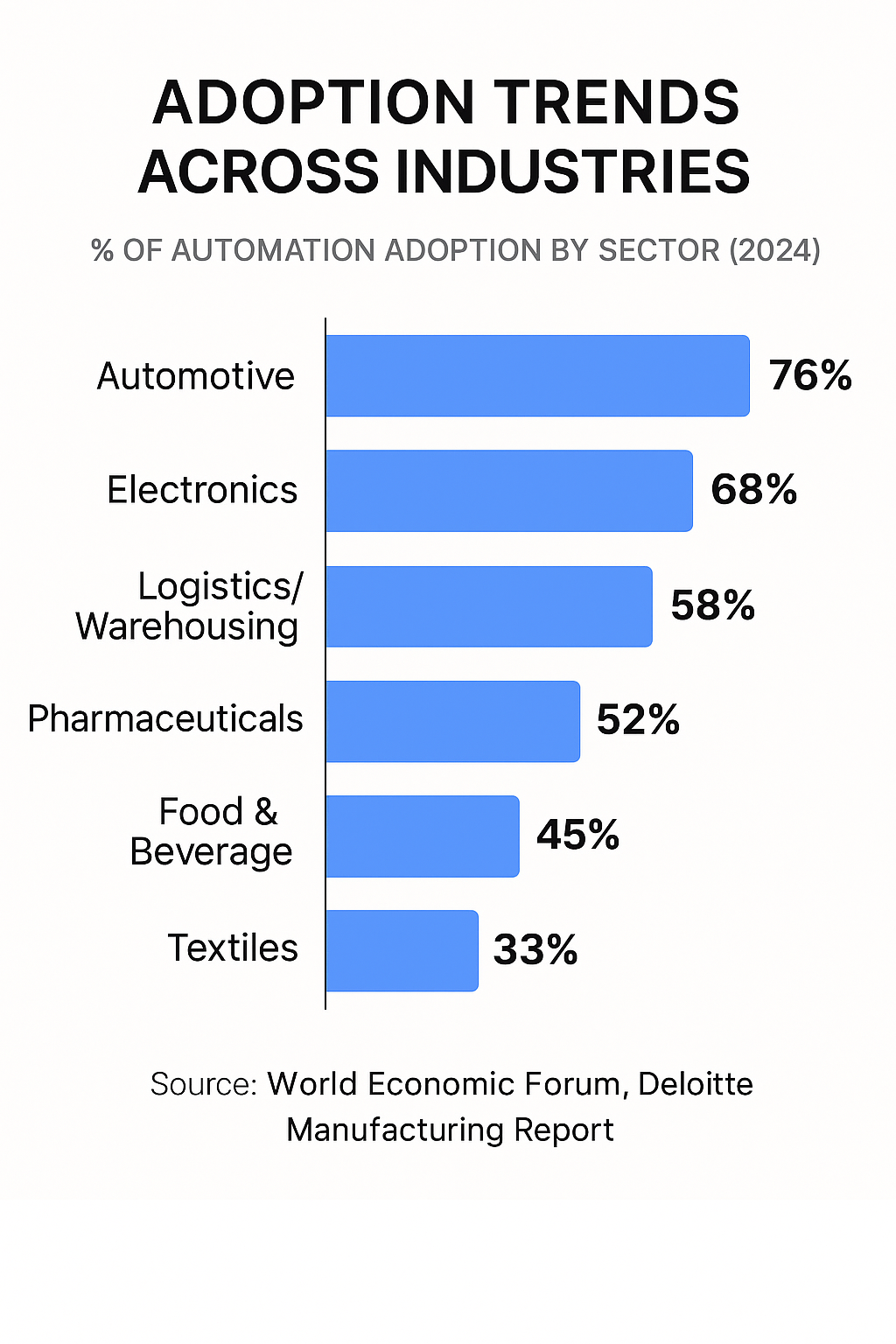
Adoption Trends Across Industries
% of Automation Adoption by Sector (2024)
• Automotive — 76%
• Electronics — 68%
• Food & Beverage — 45%
• Pharmaceuticals — 52%
• Textiles — 33%
• Logistics/Warehousing — 58%
Source: World Economic Forum, Deloitte Manufacturing Report
Benefits of Factory Automation
-
Efficiency: Processes that took hours now take minutes.
-
Safety: Dangerous tasks handled by machines reduce workplace injuries.
-
Scalability: Companies can increase production without a proportional rise in labor.
-
Customization: Smart systems allow batch-of-one manufacturing—mass production with personalized specs.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the benefits, automation brings serious challenges:
-
Job displacement: Repetitive labor roles are declining rapidly.
-
Reskilling gap: Workers need new technical competencies to remain relevant.
-
Cybersecurity: Connected factories are vulnerable to hacking and data breaches.
-
Cost barriers: Small manufacturers may struggle with upfront investment in automation technologies.
The Future: Human + Machine, Not Human vs. Machine
Factories of the future won’t be devoid of people—they’ll be filled with augmented humans. Workers will supervise AI systems, interpret complex data, and manage exceptions beyond a machine’s grasp.
🚀 The Smart Factory Ecosystem:
[IoT Sensors] → [Data Aggregation] → [AI Decision Engine] → [Automated Action] → [Human Oversight] → [Continuous Feedback Loop]
This ecosystem is self-improving. The more data it receives, the better it becomes—making factories not just productive, but adaptive.
Final Thoughts
Automation is not just a technological upgrade—it is a cultural and economic shift that redefines what it means to manufacture. While it introduces friction in the short term—especially for labor markets—it also unlocks unparalleled opportunities in innovation, safety, and global competitiveness. The real question is not whether factories will automate, but how society will steer that transformation to ensure a just and prosperous future for all stakeholders.
Smart factories are being built today. The smart policies, skills, and ethics that govern them must follow closely behind.






